Dragging heavy carts across a warehouse floor leads to exhausted workers and damaged equipment. Often, the root cause isn't the weight of the load but the material of the wheel. Choosing the wrong wheel material increases rolling resistance and accelerates wear on your expensive facility floors.
The decision typically comes down to two primary materials, and understanding the trade-offs is vital for operational efficiency. You need to balance load capacity against noise reduction and durability against floor protection. Making the wrong choice results in frequent replacements and potential safety hazards.
In this guide, we break down the critical differences between polyurethane casters vs rubber to help you specify the right component. We will compare them across load capacity, durability, and environmental resistance so you can make a data-backed decision for your facility.
Key Takeaways
Load Capacity Winner: Polyurethane. Handles 2,000+ lbs per caster; rubber tops out around 500 lbs before compression issues.
Durability Winner: Polyurethane. Resists flat-spotting, chunking, and abrasion; rubber wears faster in rough industrial settings.
Noise & Cushioning Winner: Rubber. Superior shock absorption and silent operation; polyurethane transmits vibration.
Chemical Resistance Winner: Polyurethane. Survives oil, grease, and solvents; rubber degrades quickly with chemical exposure.
Cost Trade-off: Polyurethane costs more upfront but lasts 2-3x longer (better ROI). Rubber is cheaper initially but requires frequent replacement.
The Decision: Choose polyurethane for heavy loads, chemical exposure, or long-term durability. Choose rubber for quiet zones, delicate floors, and light-duty transport.
What Are Polyurethane Casters?
Polyurethane casters feature a synthetic material molded onto a metal or plastic core. They bridge the gap between plastic and rubber, offering the durability of metal with the floor protection of rubber. They are the industrial standard for heavy-duty applications.
Advantages:
High Load Capacity: Polyurethane is a dense material that resists compression. It can carry significantly more weight per square inch than rubber without deforming. This makes it ideal for heavy machinery and fully loaded pallet carts.
Superior Wear Resistance: These wheels resist abrasion, tearing, and chunking. They maintain their shape even after miles of travel over rough concrete. This durability translates to fewer replacement cycles and lower maintenance costs.
Excellent Floor Protection: Despite being harder than rubber, polyurethane deflects enough to prevent scratching or marking. It protects expensive epoxy and concrete floors from the damage typically caused by steel or cast-iron wheels.
Chemical and Oil Resistance: Polyurethane does not break down when exposed to oils, grease, or mild acids. This resistance makes it suitable for automotive plants and machine shops where spills are common.
Low Rolling Resistance: The material's firmness ensures it does not flatten under load. This reduces the push-pull force required to move equipment. Lower resistance improves ergonomic safety for operators moving heavy loads manually.
While polyurethane excels in strength and durability, it is often too rigid for sensitive environments. Next, we examine the specific characteristics of the softer alternative.
What Are Rubber Casters?
Rubber casters consist of natural or synthetic rubber bonded to a central hub. They are known for their softness, elasticity, and ability to cushion loads. They are the preferred choice for light-to-medium duty applications requiring quiet operation.
Advantages:
Maximum Noise Reduction: Rubber is soft and absorbs vibration naturally. It rolls silently over tile, concrete, and uneven surfaces. This is critical in hospitals, libraries, and retail environments where noise pollution is a concern.
Shock Absorption: The elasticity of rubber cushions the load against bumps and cracks in the floor. This protects sensitive electronics, glass, or fragile cargo during transport. It acts as a suspension system for your cart.
Debris Rejection: Soft rubber tends to roll over small debris like metal shavings or screws rather than embedding them. This prevents the wheel from becoming a grinding tool that damages your floor finish.
High Traction: Rubber provides excellent grip on wet or slick surfaces. This prevents carts from sliding out of control on ramps or damp loading docks. It enhances control and safety in unpredictable environments.
Cost-Effective Solution: For general-purpose, light-duty applications, rubber casters are often more affordable upfront. They provide a high-value solution for equipment that does not require extreme load capacities.
Confused about polyurethane vs rubber for your operation? Humphries Casters has sourced solutions across 400+ factories for 37 years. Contact us for help.
Knowing the individual advantages is only half the battle. To select correctly, you must compare these two materials across eight crucial performance criteria.
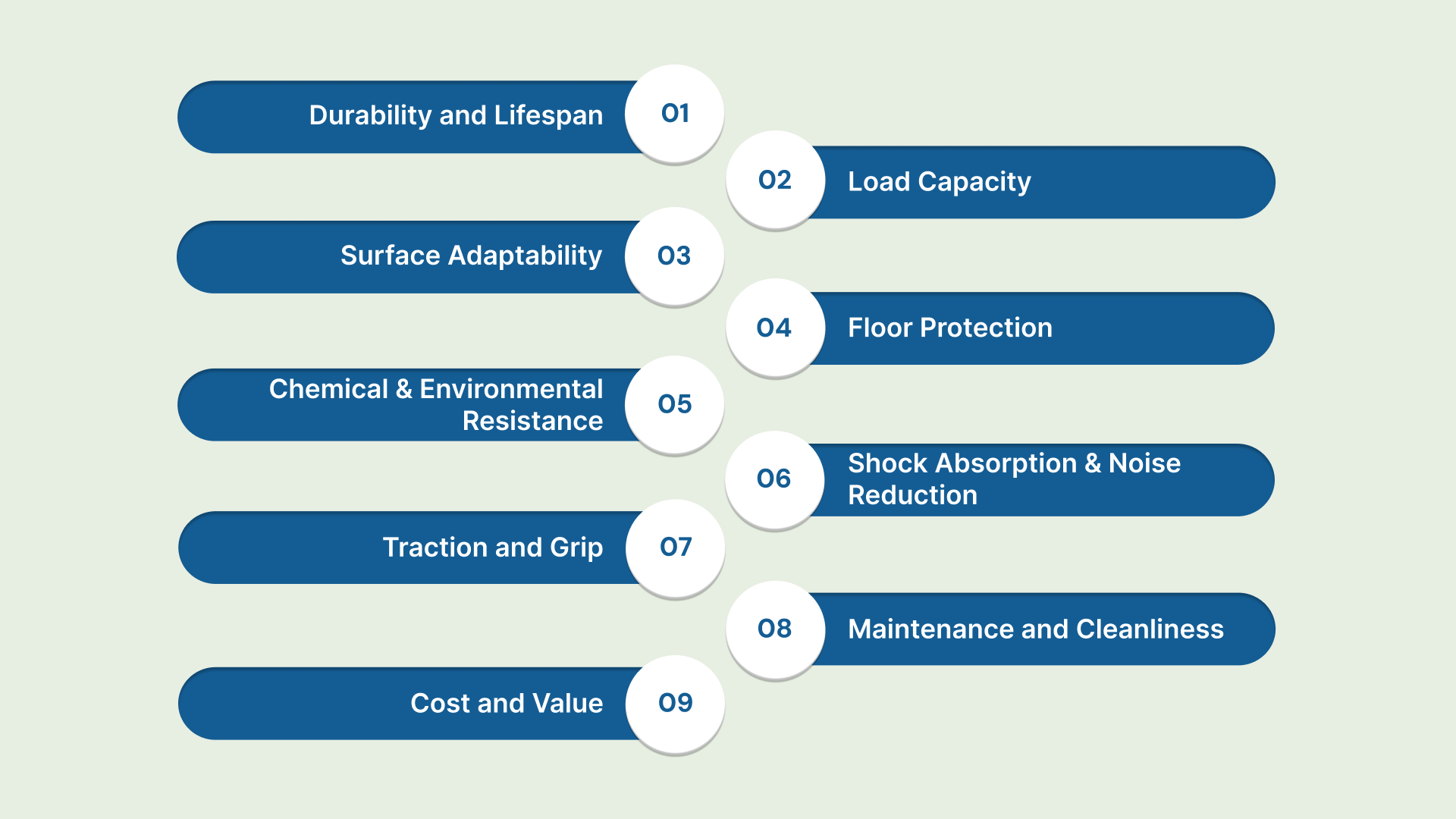
Polyurethane vs Rubber Casters: 8 Key Differences
Understanding the technical distinctions ensures you select the material that aligns with your specific operational environment. Here is how polyurethane and rubber compare across critical performance categories:
Durability and Lifespan
Polyurethane is engineered to withstand abrasion and cutting, lasting significantly longer in rough environments. Rubber wears down faster and is prone to chunking if used on rough terrain.
Polyurethane Casters:
Resist flat-spotting even when left stationary under heavy loads.
Withstand abrasive concrete and metal shavings without tearing.
Maintain structural integrity for years in high-cycle manufacturing.
Rubber Casters:
Prone to developing flat spots if left loaded for long periods.
Can chunk or tear when turning sharply on rough surfaces.
Generally require more frequent replacement in industrial settings.
Load Capacity
Load capacity is the most distinct difference; polyurethane is for heavy lifting, while rubber is for lighter, cushioned transport.
Polyurethane Casters:
Handle extreme weights, often exceeding 2,000 lbs per caster, depending on size.
Maintain shape under maximum load, ensuring consistent rollability.
Ideal for heavy tooling fixtures and aerospace assembly.
Rubber Casters:
Best suited for loads under 500 lbs per caster.
Compress under a heavy weight, which increases the force needed to push.
Used primarily for hand trucks, waste bins, and light carts.
Surface Adaptability
The texture and condition of your flooring dictate which material will perform best without causing damage or safety issues.
Polyurethane Casters:
Perform best on smooth, hard surfaces like finished concrete and epoxy.
Can damage soft flooring like linoleum if the load is too heavy.
Roll over small cracks easily but transmit vibration to the cart.
Rubber Casters:
Adapt well to uneven, cracked, or outdoor surfaces.
Provide a smooth ride over thresholds and elevator gaps.
Safe for use on almost all flooring types, including carpet and wood.
Floor Protection
Protecting your facility's floor is a major ROI factor; repairing epoxy or polished concrete is expensive.
Polyurethane Casters:
Distribute weight effectively to prevent indentations on concrete.
Will not mark floors, provided the wheel is kept clean.
Prevent the "grinding" effect caused by harder nylon or steel wheels.
Rubber Casters:
Grey (thermoplastic) rubber is non-marking and safe for tile/vinyl.
Black rubber can leave unsightly carbon marks on light-colored floors.
Reject debris, preventing metal chips from being ground into the floor.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Industrial environments often contain solvents and temperature fluctuations that attack wheel materials.
Polyurethane Casters:
Impervious to grease, oil, and most industrial cleaning solvents.
It can be formulated to withstand specific pH levels.
Perform well in standard warehouse temperature ranges.
Rubber Casters:
Degrade quickly when exposed to oil, turning soft and spongy.
Synthetic rubber (TPR) offers better resistance than natural rubber.
Certain rubber compounds work better in outdoor UV exposure.
Shock Absorption and Noise Reduction
For environments requiring silence or cargo protection, the wheel material acts as the primary dampener.
Polyurethane Casters:
Harder durometer leads to a noisier ride compared to rubber.
Transmits vibration, making them less ideal for fragile electronics.
Newer "soft poly" formulations exist to bridge this gap.
Rubber Casters:
The undisputed leader in quiet operation.
Absorbs impacts, reducing rattling of the cart and its contents.
Essential for healthcare (HCAHPS scores) and customer-facing zones.
Traction and Grip
Control is a safety issue; wheels that slide on wet floors cause accidents.
Polyurethane Casters:
A lower coefficient of friction allows for easier sliding/maneuvering.
It can be slippery on smooth, wet floors.
Great for tight turns in dry environments.
Rubber Casters:
A high friction coefficient provides "grip" on the floor.
Prevents equipment from drifting on slight inclines.
Offers superior stopping power on wet or slick surfaces.
Maintenance and Cleanliness
Hygiene and maintenance cycles impact the total cost of ownership.
Polyurethane Casters:
A smooth surface is easy to wipe down and clean.
Resists bacterial growth better than porous natural rubber.
Rarely shed material, keeping cleanrooms free of particulate.
Rubber Casters:
It can become brittle and crack over time, shedding rubber particles.
The porous nature can trap dirt and moisture.
Require inspection for dry rot in older equipment.
Cost and Value
Budgeting involves looking at the initial purchase price versus long-term replacement costs.
Polyurethane Casters:
Higher initial investment per unit.
Longer lifespan reduces the frequency of replacement orders.
Better ROI for heavy-duty, daily-use industrial equipment.
Rubber Casters:
Lower entry price point helps with immediate budget constraints.
A shorter lifespan may increase long-term operational costs.
Best value for low-use or light-duty equipment.
In summary:
Feature | Polyurethane Casters | Rubber Casters | Primary Use Case |
1. Load Capacity | Excellent: Supports extreme loads (often over 2,000 lbs). | Fair: Best suited for light loads (under 500 lbs); compresses under heavy weight. | Heavy Industrial |
2. Durability / Lifespan | Superior: Highly resistant to flat-spotting, chunking, and abrasion. | Moderate: Prone to flat-spotting and faster wear in rough, high-cycle use. | Longevity & Uptime |
3. Shock Absorption | Low: Transmits vibration; harder durometer leads to a noisier ride. | Excellent: Undisputed leader in quiet operation and dampening impact. | Fragile Cargo / Quiet Zones |
4. Chemical Resistance | High: Impervious to oil, grease, and most industrial cleaning solvents. | Low: Degrades quickly when exposed to oils or many solvents. | Machine Shops / Automotive |
5. Rolling Resistance | Low: Firmness ensures low push-pull force, improving staff ergonomics. | High: Softer material compresses, increasing the effort needed to push carts. | Staff Ergonomics |
6. Floor Protection | High: Non-marking and distributes heavy weight to prevent floor indentations. | High: Excellent debris rejection; non-marking grey options available for tile. | Sensitive Floors |
7. Surface Adaptability | Best for smooth, finished surfaces like epoxy or concrete. | Best for uneven, cracked, or outdoor surfaces; cushions the ride over gaps. | Uneven Terrain |
8. Cost and Value | Higher initial investment, but offers better long-term ROI due to longevity. | Lower initial cost, but shorter lifespan increases long-term replacement frequency. | Budgeting Strategy |
These technical differences directly influence performance on the warehouse floor and in specialized settings. Now, let us look at the specific industries that rely on each wheel type.
Industrial Applications of Rubber and Polyurethane Casters
Selecting the right caster depends heavily on the specific industry vertical. Here is how different sectors utilize these materials:
Polyurethane Casters Applications
Ideal for heavy-duty manufacturing, warehousing, and environments with chemical exposure.
Manufacturing & Warehousing: Heavy pallet racks, tow lines, and production dollies carrying raw materials.
Automotive & Aerospace: Tooling carts and assembly fixtures requiring high load capacity and floor protection.
Rubber Casters Applications
Best for environments needing quiet, cushioned transport and light loads.
Healthcare & Institutional: Medical carts, hospital beds, and library carts where silence is critical.
Office & Light Commercial: Furniture dollies, hand trucks, and delivery carts used on mixed surfaces.
Your industry has unique demands. Humphries Casters works with caster and wheel factories around the globe, so we can offer you the right caster at the right price. Contact us now for a customized order.
Understanding industry best practices is a great starting point, but your final choice must be based on an internal audit. Here is a framework for precise selection.
How to Choose the Right Caster for Your Industrial Needs?
To select the correct wheel, you must audit your facility's specific conditions. Focusing on load, floor type, and ergonomics prevents failure.
Here are the critical factors to evaluate before purchasing:
Calculate the Total Load Requirements: Determine the maximum weight of the cart plus the payload. Divide this total by three (not four) to account for uneven floors. If the load per wheel exceeds 500 lbs, polyurethane is usually the required choice for safety.
Audit Your Floor Conditions: Inspect your facility for debris, cracks, and surface type. If the floor is covered in metal shavings or oil, use polyurethane. If the floor is pristine tile or requires noise dampening, rubber is the safer option.
Assess Environmental Exposure: Identify any chemicals, temperatures, or moisture present. Polyurethane is necessary for areas with oil or grease. Rubber or specialized pneumatic options are better suited for outdoor or uneven terrain.
Factor in Ergonomics and Push Force: Consider who is moving the equipment. If operators manually push carts all day, the lower rolling resistance of polyurethane significantly reduces fatigue and injury risk compared to softer rubber.
Even with a clear selection framework, non-standard loads or environmental factors can make purchasing complex. This is where specialized support is essential.
Humphries Casters: Solving the Material Dilemma
Choosing between polyurethane and rubber often feels like a compromise between durability and noise control. Off-the-shelf catalogs force you to pick one standard option, even if your environment demands a specific blend of softness and chemical resistance.
Humphries Casters eliminates this compromise. We assess your specific facility conditions, flooring type, chemical presence, and noise targets to recommend the exact wheel formulation you need.
Custom Formulations: We can source softer polyurethane blends that offer the grip of rubber with the durability of poly.
Global Sourcing: Access to 400+ factories ensures we find the perfect tread-to-core bond for your specific load.
Ergonomic Focus: We prioritize wheels that lower push/pull forces, reducing injury risk for your team.
Unbiased Advice: As a manufacturer and distributor, we recommend the material that works, not just what we have in stock.
We help you consolidate your supply chain while upgrading the performance of your material handling equipment.
Conclusion
Polyurethane casters offer superior durability, load capacity, and chemical resistance for industrial use. Rubber casters provide the best cushioning, noise reduction, and traction for lighter, sensitive applications.
Choosing the wrong one leads to frustrated staff, damaged floors, and frequent replacement costs. By matching the material properties to your specific environment, heavy loads vs. quiet zones, oil exposure vs. clean floors, you ensure operational efficiency and safety.
Humphries Casters leverages decades of experience to analyze your facility's needs and supply the exact mobility solutions that keep your business moving.
Contact us today to discuss your material handling challenges and improve your operational efficiency.
FAQs
Q. Which is better for outdoor use, rubber or polyurethane?
Rubber is generally better for outdoor use. Its softness absorbs shock from uneven pavement, gravel, and debris. Polyurethane is often too hard and can transmit vibration or chip on rough asphalt.
Q. Can polyurethane casters be used on hardwood floors?
Yes, polyurethane is excellent for hardwood floors. It is non-marking and distributes weight well, preventing scratches and gouges that harder nylon or metal wheels would cause.
Q. Why do my rubber casters leave black marks?
Standard black rubber contains carbon black, which can mark floors. To avoid this, specify "non-marking grey rubber" or switch to polyurethane, which is inherently non-marking.
Q. Do polyurethane casters have flat spots?
High-quality polyurethane resists flat-spotting much better than rubber. However, leaving a very heavy load stationary for weeks can still cause minor deformation. Rubber flattens much faster.
Q. Is polyurethane resistant to all chemicals?
Polyurethane resists oils, grease, and many solvents, but strong acids or bases can damage it. Always check a chemical compatibility chart for your specific exposure risks.